HACCP Guide - Definition, Templates, and the 7 Principles of Safe Food Handling
In this article, you will learn what HACCP means and how you can implement the 7 principles of the HACCP concept. We also share helpful tips, provide a template, and show concrete examples that you can use for your e-commerce business. Finally, you will gain insight into what optimised fulfilment of organic products can look like.
What is HACCP? Meaning and Definition of the Food Hygiene Concept
The abbreviation HACCP stands for Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point. It is a concept that, under the EU Regulation (EC) No. 852/2004 on food hygiene, ensures the protection of consumers when buying food. It requires traders who produce, process, or distribute food to set up and adhere to HACCP measures.
Guide to Compliance with the HACCP Concept
To simplify the concept and provide clear guidance, the HACCP system is divided into 7 principles. Start by selecting a HACCP team comprising members from different departments, if possible, to develop a product description that includes the following data:
- Food
- Ingredients
- Processing method
- Packing
- Storage
- Distribution methods (frozen, room temperature...)
- Label and label information
- Target group
.png?width=960&name=HACCP%20(5).png)
Before the team begins with the first of the 7 principles, a flow chart should be created. We have provided an example for you.
.png?width=1920&name=HACCP%20(6).png)
The 7 Principles of the HACCP Concept
To make these steps easier to follow, we have created a simple example. Feel free to use it for inspiration or download our HACCP template for free.
Principle 1: Conducting a Hazard Analysis
Firstly, list all steps of the process and identify potential risk factors.
Types of food safety risks
|
Type of risk |
Examples |
Control & Risk Mitigation |
|
Chemical |
Allergens, pesticide residues |
Cleaning, Purification |
|
Biological |
Salmonella, parasites, pests |
Temperature management |
|
Physical |
Dust, metals, plastic |
Sieves, metal detectors |
|
Humane |
Work overload, Low qualification |
Testing and training |
Principle 2: Identifying Critical Control Points (CCP)
A critical control point is a step where a controlled operation can reduce, avoid, or eliminate food-related risks to an acceptable level. In this step, your dedicated HACCP team uses a decision tree to identify such CCPs.
Sometimes, a single process step may require multiple CCPs, while in other instances, one CCP may be used for more than one food hazard.
Resource: The CCP Decision Tree
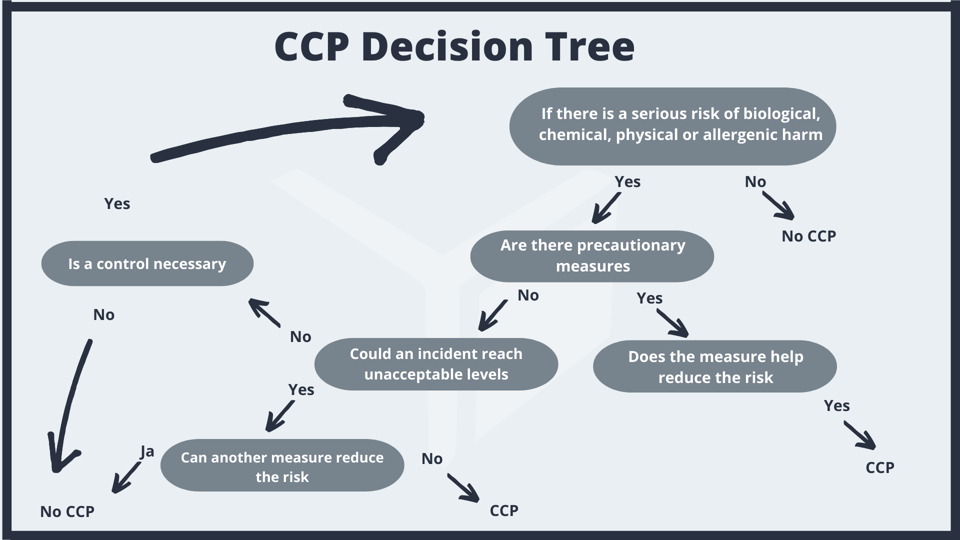
Principle 3: Establishing Critical Limits
A critical limit (CL) is the maximum or minimum value to which a biological, chemical, or physical parameter must be controlled at a CCP to prevent, eliminate, or reduce a food safety hazard to an acceptable level. These limits are measured at CCPs and typically involve units such as temperature, time, weight, pH, and other scientific standards.
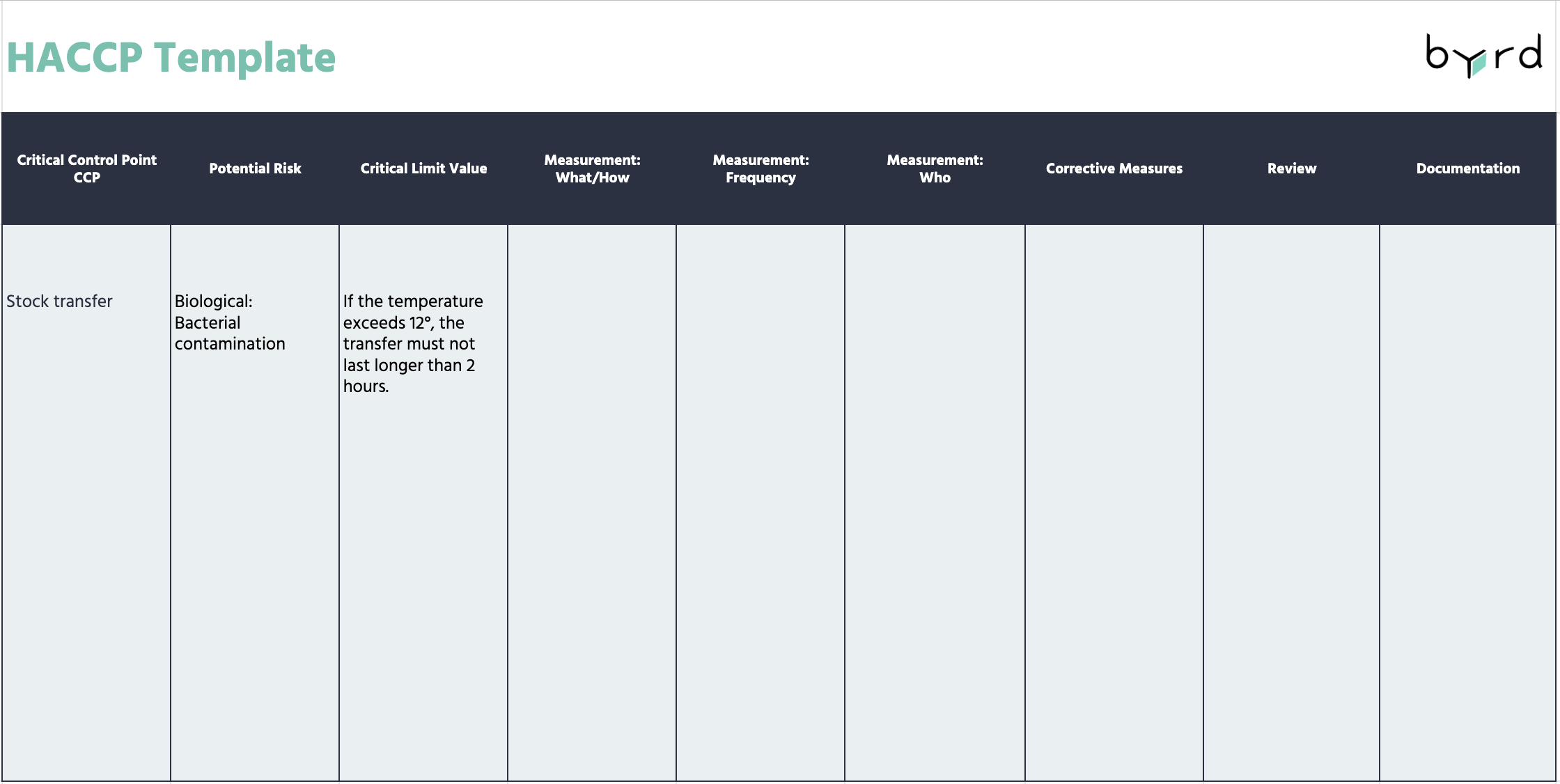
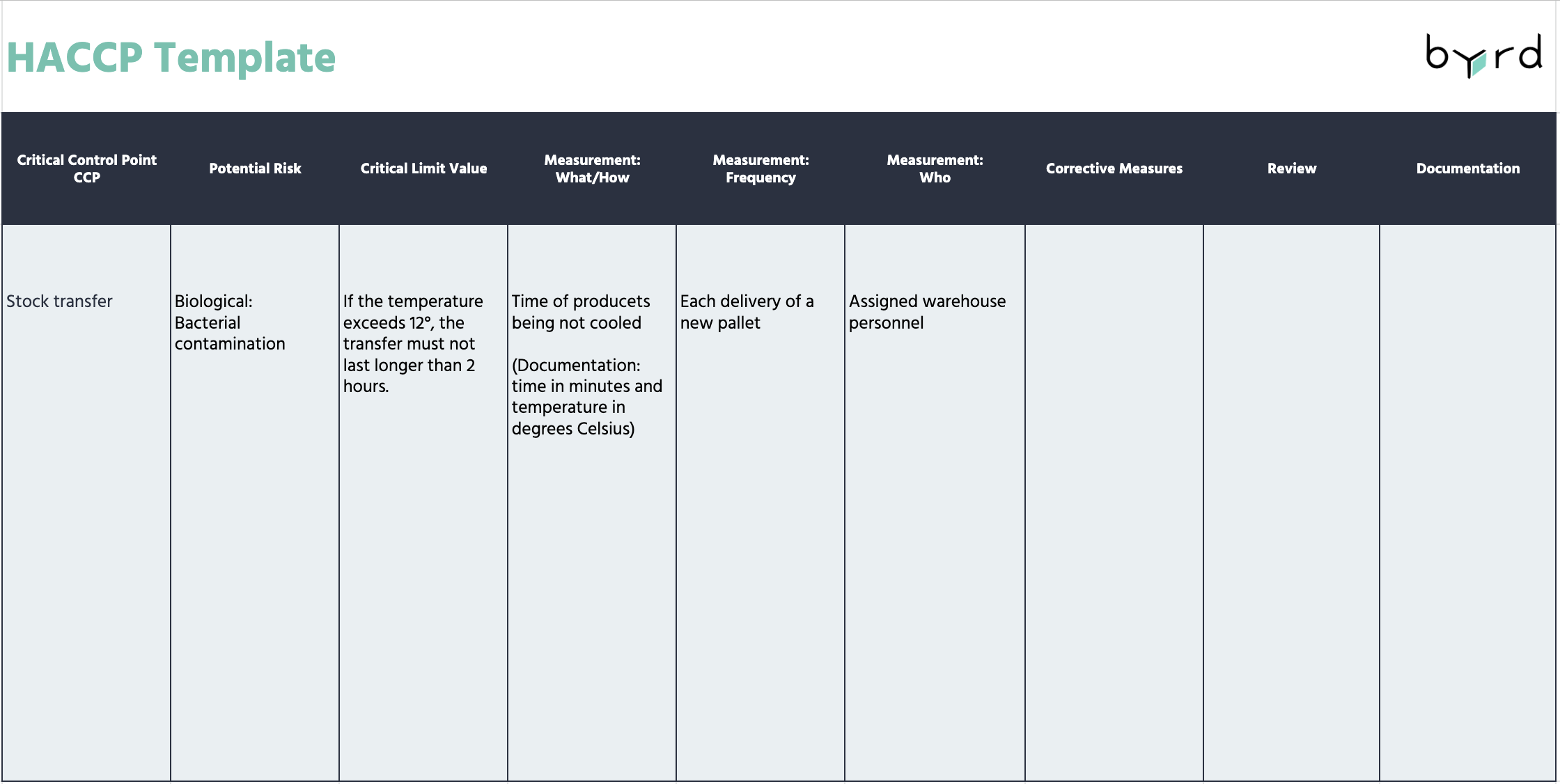
Principle 4: Monitoring Critical Control Points (CCPs)
In this step, the HACCP team outlines how to monitor CCPs. The process should include detailed descriptions of the following:
- Measurement procedure
- Time of the measurement
- Responsibility for the measurement
- Frequency of measurements
Principle 5: Implementing Corrective Actions
Corrective actions are necessary when a critical limit is exceeded or not met. The priority is to prevent the product from entering the food chain. Additionally, a failure analysis is conducted to identify any weaknesses in the process and prevent the problem from recurring.
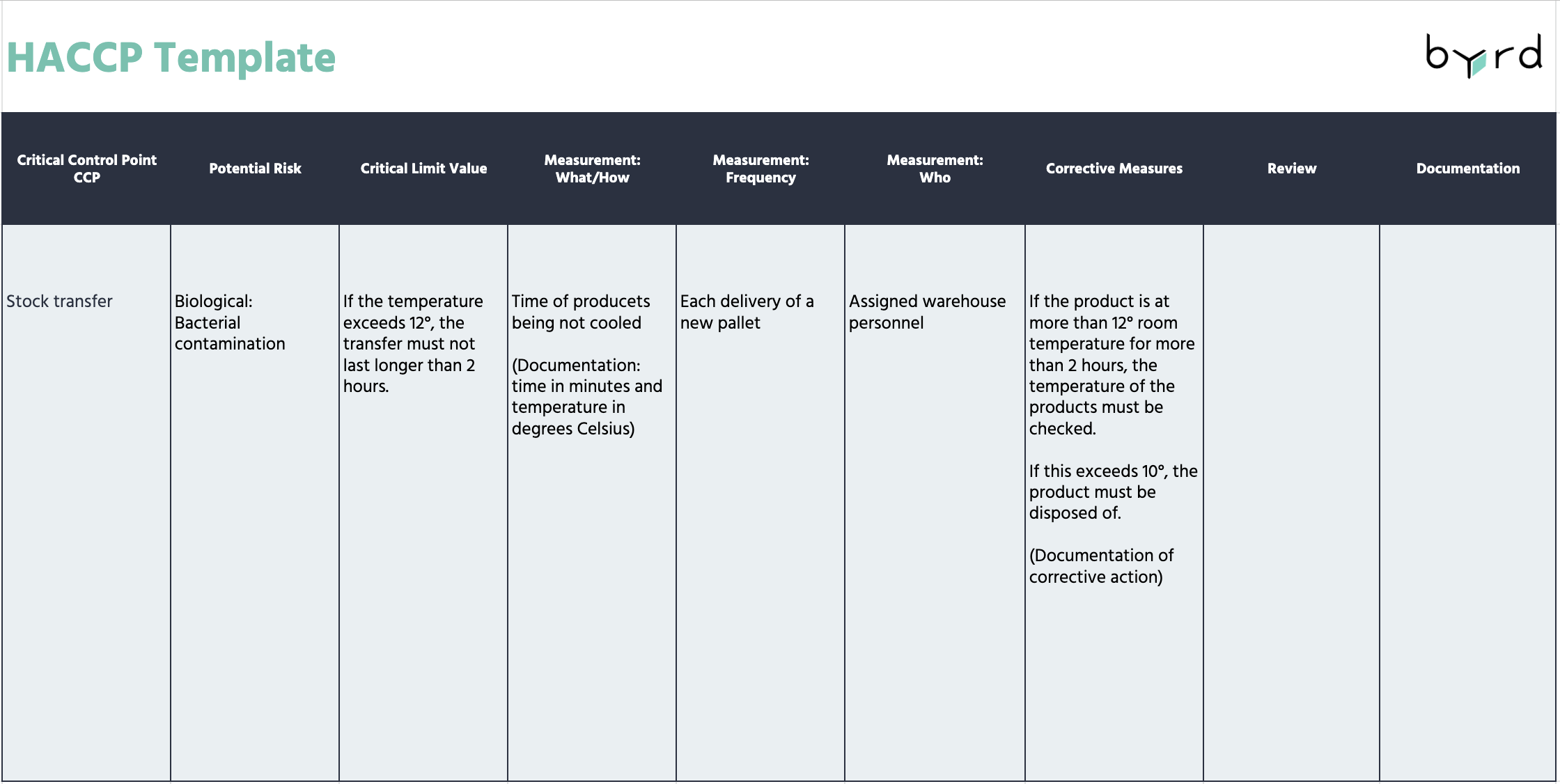
Principle 6: Verifying the HACCP System
To ensure the HACCP system remains effective and accurate, it is crucial to regularly review and validate all aspects of the process. This includes challenging CCPs, checking measuring devices, and critically assessing past performance.
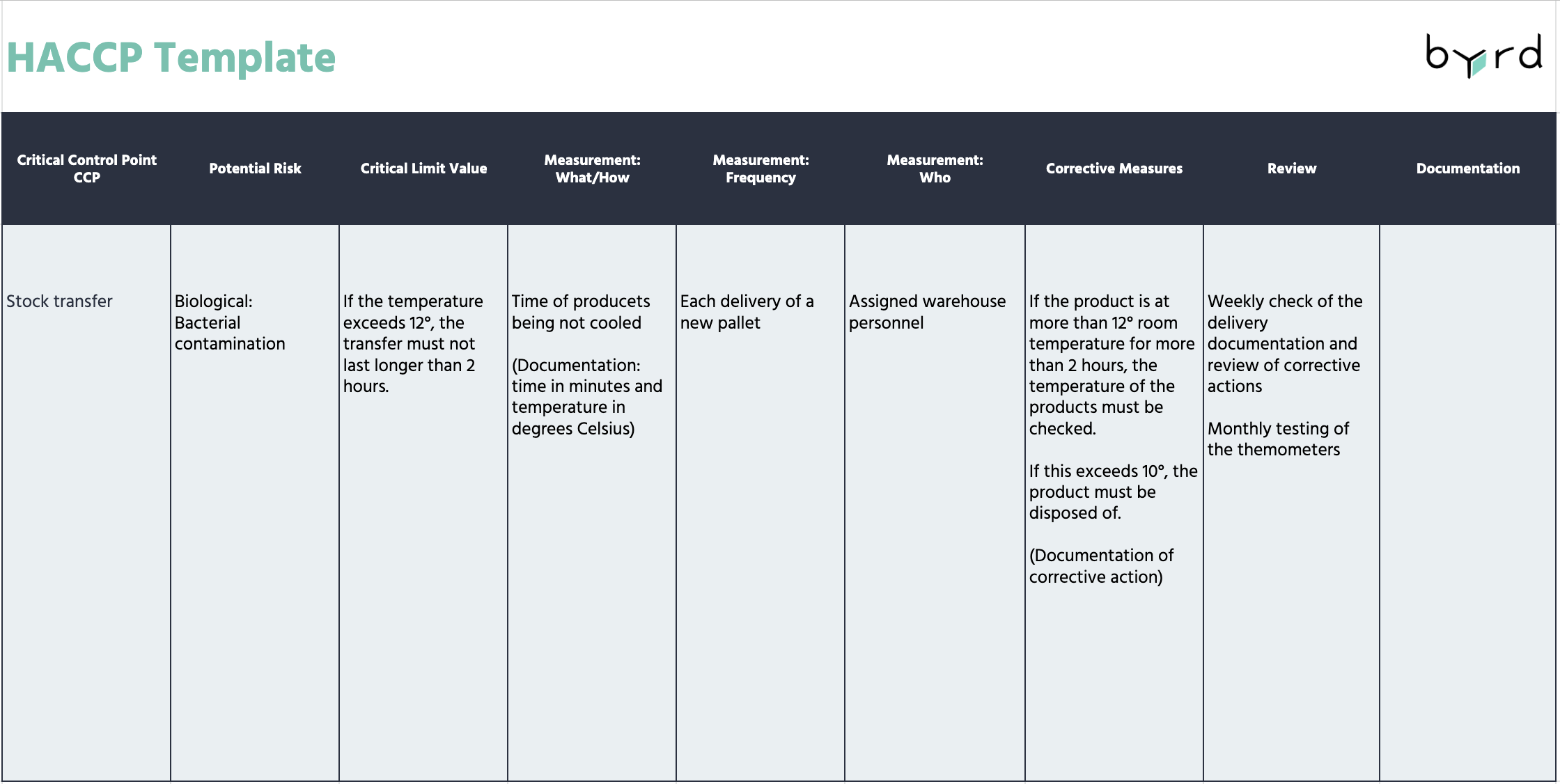
Principle 7: Documentation
Accurate record-keeping is a fundamental part of the HACCP system. Documentation can be used to prove that food has been produced, stored, and transported safely. Records should include:
- HACCP team members
- Hazard analysis
- Product description
- Critical control points
- Critical limits
- Monitoring systems
- Corrective actions
- Review process
- Documentation process
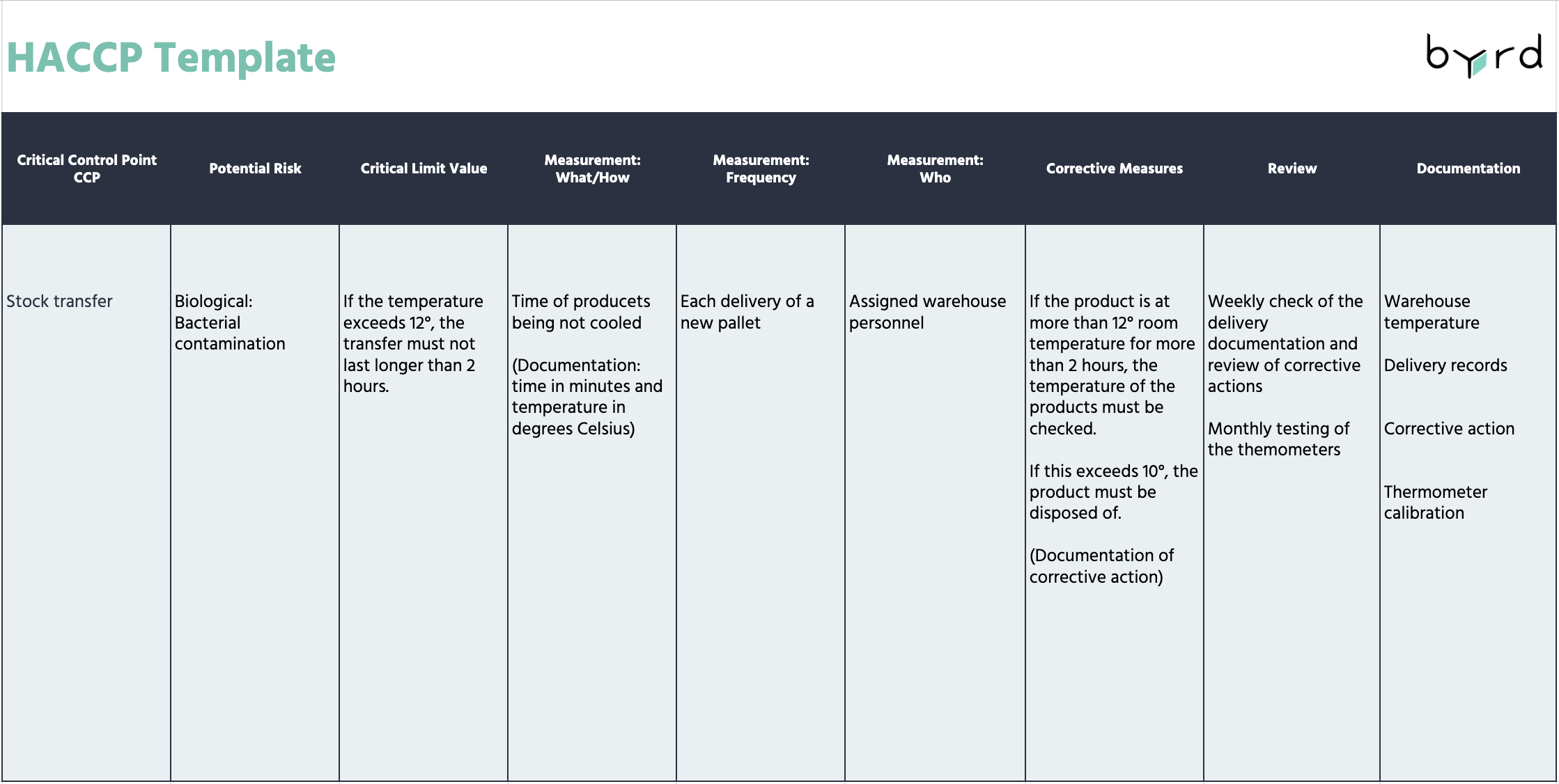
Legal Consequences of Non-compliance with the HACCP Concept
The safety and health of consumers are paramount. Therefore, non-compliance with the HACCP concept can result in severe penalties. These can range from mandatory training for the responsible team to imprisonment for distributing dangerous food. Other penalties include the forced closure of a business and various fines for hygiene violations.
HACCP Template
To simplify the process we offer you the chance to download our HACCP template for free.
Fulfillment of Organic Products
Are you selling organic products online and seeking the right fulfilment solution? Byrd could be the ideal partner for you. Besides working with comparatively climate-friendly parcel services and offering climate-neutral shipping options, byrd’s logistics centres are equipped to handle organic products.
This includes all necessary certifications and the capability for LOT tracking to better manage batches.
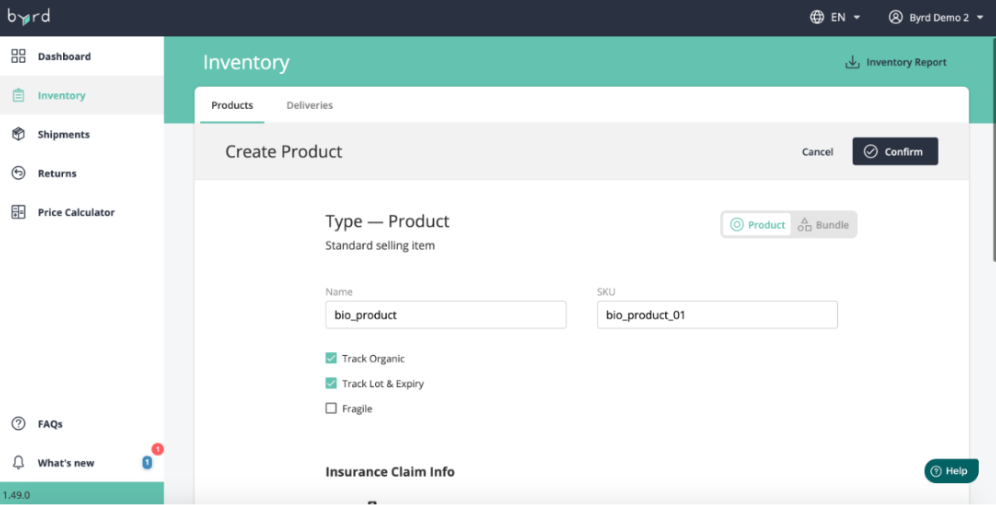
Once your store is connected to Byrd, you can easily customise your items in our user-friendly fulfilment dashboard. Simply click on "Track Organic" and "Track Lot & Expiry" to get started.
What don’t we offer? As of July 2022, we do not handle the storage and shipping of frozen items. However, we can efficiently manage climate-controlled products.
Two of our many satisfied customers using these services are Your Super and Primal State. Feel free to explore their and other success stories that we have proudly contributed to.

