The Customs Form Made Easy
Whether you're sending a package as a private individual or as a business, dealing with the customs form (CN22 or CN23) can be daunting. However, handling customs shipments doesn't have to be complicated! This guide aims to simplify cross-border e-commerce and fulfilment for you.
When Do I Need to Include a Customs Form When Shipping?
A customs form is required for any consignment sent to a country outside the EU. For goods valued up to €425 (in 2024 for parcels up to 2kg), the CN22 form suffices. For shipments exceeding this amount, the detailed CN23 form is necessary. This blog will focus on the CN23 form, which can also complement the CN22. Ensure the form is attached to the outside of the shipping box, ideally enclosed in a transparent, self-adhesive sleeve. Additionally, for sold goods, a commercial invoice and a copy must be included.
How to Correctly Fill in the Customs Declaration - CN23 Made Easy
The key is to ensure the information is clear and understandable to customs officials in the receiving country. Therefore, it must be in English or the respective national language. The fields on the customs form should be labelled as follows:
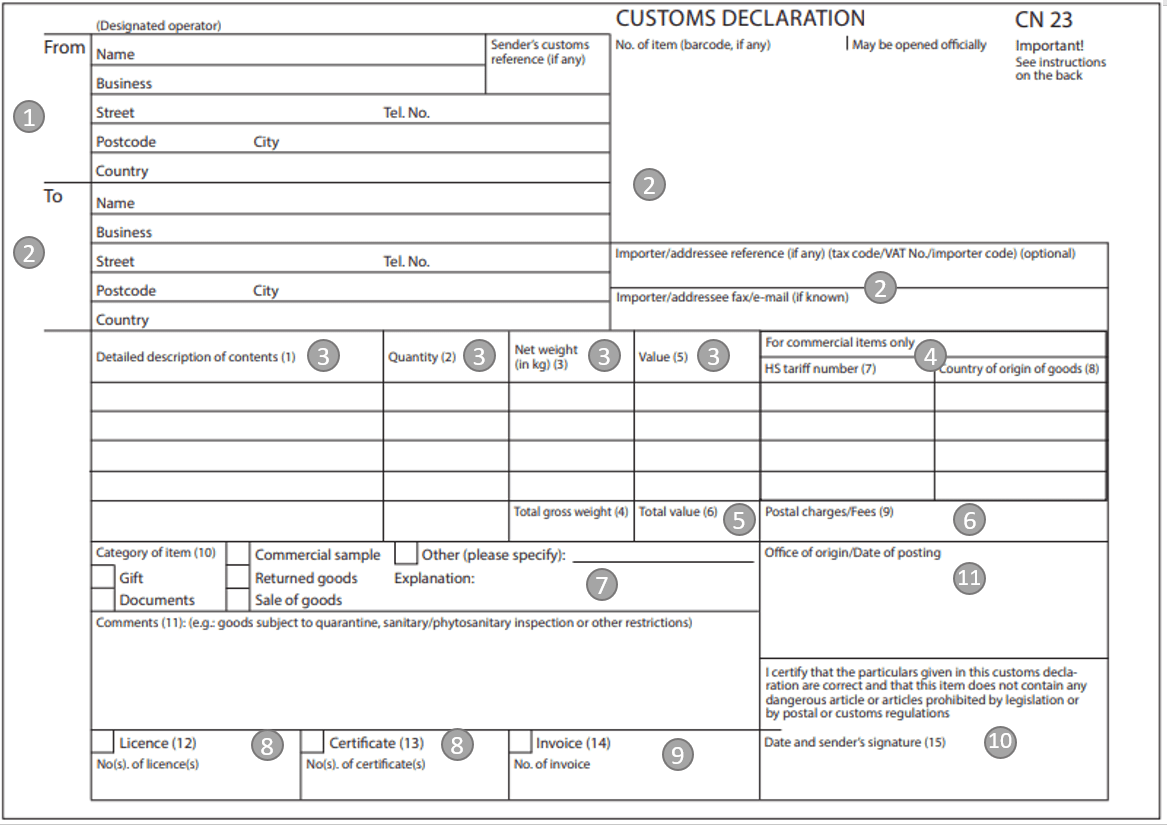
- Sender Data:
Provide the sender's address and, if possible, a telephone number. If it's a private consignment, the customs number (EORI) field remains empty and only needs to be filled by companies. If you don't have a customs number, you can find more information on how to apply here:
- Recipient Data:Enter the recipient's address again, even if it's already on the parcel label, and include the country of destination. For commercial sales, list the VAT ID to the right and add additional contact information below this.
- Quantity, Description, Weight, Value, Currency Unit: Provide detailed information about the goods. For similar items, sum up the quantity, weight, and value.
- Customs Tariff Number and Country of Origin: This is mandatory for commercial goods but not for gift consignments. The customs tariff number corresponds to the HS code and is used to identify goods in foreign trade statistics. You can find a list of all customs tariff numbers here. The country of origin refers to the country where the goods were manufactured.
- Total Weight and Value of the Goods: Add up the values from the previous fields. The total value should match the commercial invoice for commercial shipments.
- Postage Costs: Customs duties in the recipient country are calculated based on the value of the goods plus postage costs. Indicate the postage costs in the currency of the destination country if the recipient pays for shipping. If the delivery is free, this point is not applicable.
- Type of Shipment: Tick the appropriate box and state in the "Declaration" field, for example, that it's an "Article for sale".
- Remarks, Certificates, Approvals: This field is for goods requiring authorisation to a non-EU country. This can be complex and should be managed by experts.
- Invoice Number: If you're selling goods, include a commercial invoice and its corresponding number here.
- Date and Signature of the Sender: Fill in the date and sign the form.
- Depository and Date of Dispatch: This will be completed by the shipping company or post office.
To clarify, here is an example. If you own an online shop and are sending two T-shirts (€19.90 each) and a pair of jeans (€70.00) to Switzerland, the customs form should be filled out as follows:
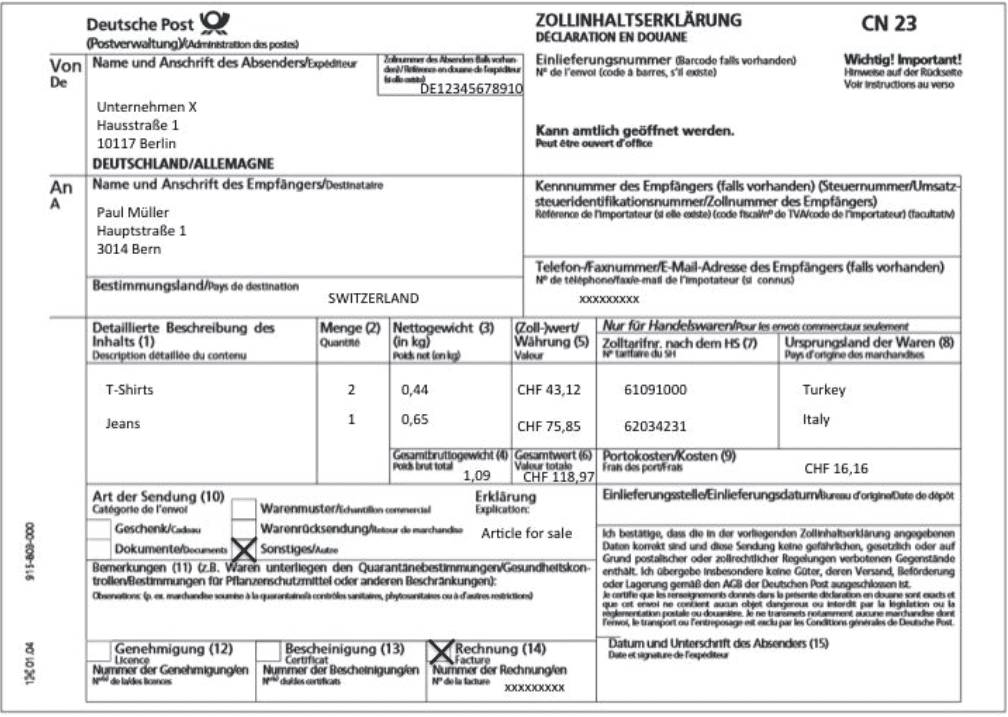
Following these instructions will ensure your shipment to a third country is processed smoothly.
Is the customs process too tedious? byrd helps you to quickly and easily complete customs clearance. We take care of the entire fulfilment process. Just connect your sales channels, send us your stock and we take care of the rest.
You can find more information about our service here: getbyrd.com
